Speed Test
Internet Speed Test service is provided by speed test to check the speed of your internet . You can check the download speed as well as upload speed of your internet in fastest and secure way. We provide the internet speed informationn from our inbuild tool.To keep our user secure , we never store any user information.
How To Check Internet Speed?
Our Internet Speed Test service allows you to check the Internet Speed information of your internet provider easily.
- Go to https://speedtests.in
- Press "Start Speed Test" button.
- Internet speed results will be displayed instantly by speed test tool instantly.
- You can find download speed, upload speed , ping time and jitter of your internet.
- Your data and privacy is fully protected. We don't store any user information.
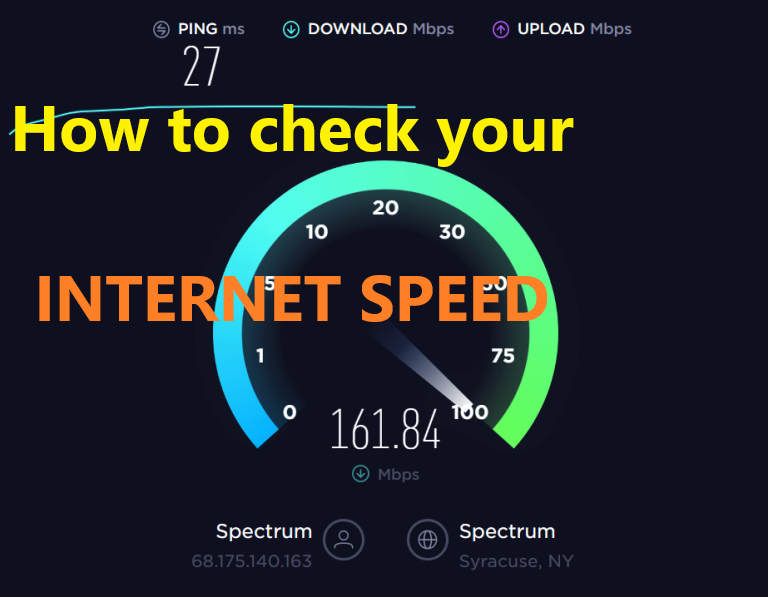
To check the information of internet, our internet speed test service is the best and secure. Our Internet speed test service is completely secure as we do not store any information or public ip number with us. Please note that we are not using any third party service to detect internet speed.We use our inbuild tool to provide internet speed information.
Internet Speed
Internet Speed is the allocated bandwidth.Bandwidth is the amount of data sent to you per second. For example 5MB/Sec means 5 mega bytes of data recived per second.
When you check your internet speed , you see four numbers i.e Download Speed, Upload Speed , Ping and Jitter.
- Download Speed:The megabits-per-second(Mb/Sec) rate by which data is transferred from the Internet to your computer.
- Upload Speed:The megabits-per-second(Mb/Sec) rate by which data is transferred from your computer to Internet.
- Ping:It is the time taken in transmiting the data packets from your device to a server on the Internet and back to your device again. The ping time is measured in milliseconds (ms).
- Jitter:It is the time delay in the sending of these data packets over your network connection. This is mainly caused by network congestion and sometimes due to route changes. The more jitter means data packet will take more time to arrive and this will impact the Video and Audio Quality.
Internet
The Internet, here and there called essentially "the Net," is an overall arrangement of PC network s – a network of network s wherein clients at any one PC can, on the off chance that they have consent, get data from some other PC (and once in a while talk straightforwardly to clients at different PCs). It was brought about by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) of the U.S. government in 1969 and was first known as the ARPANET. The first point was to make an organization that would permit clients of an examination PC at one college to "converse with" research PCs at different colleges. A side advantage of ARPA Net's plan was that, since messages could be steered or rerouted more than one way, the organization could keep on working regardless of whether parts of it were obliterated in case of a tactical assault or other fiasco.
Today, the Internet is a public, agreeable and self-supporting office open to countless individuals around the world. It is utilized by numerous individuals as the essential wellspring of data utilization, and energized the creation and development of its own social biological system through web-based media and content sharing. Moreover, web e-commerce, or online shopping, has gotten perhaps the biggest utilization of the Internet.
How the Internet functions
Truly, the Internet utilizes a part of the absolute assets of the at present existing public telecommunication networks. In fact, what recognizes the Internet is it's anything but a bunch of protocols called Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP). Two recent variations of Internet innovation, the Intranet and the extranet, likewise utilize the TCP/IP protocol.
The Internet can be viewed as having two significant parts: network protocols and hardware. The protocols, like the TCP/IP suite, present arrangements of decides that gadgets should continue to finish jobs. Without this normal assortment of rules, machines would not have the option to impart.
The protocols are additionally answerable for deciphering the alphabetic content of a message into electronic signs that can be sent over the Internet, and afterward back again into readable, alphabetic content.
Hardware, the second significant segment of the Internet, incorporates everything from the PC or smart phone that is utilized to get to the Internet to the cables that convey data starting with one gadget then onto the next. Extra sorts of hardware incorporate satellites, radios, cell phone towers,routers and servers.
These different sorts of hardware are the associations inside the network. Gadgets like PCs, cell phones and laptops are end focuses, or customers, while the machines that store the data are the servers. The transmission lines that trade the information can either be wireless signs from satellites or 4G and mobile phone towers, or physical lines, like cables and fiber optics.
The process of transferring information from one gadget then onto the next depends on packet switching. Every PC associated with the Internet is doled out an extraordinary IP address that permits the gadget to be perceived. At the point when one gadget endeavours to send a message on another gadget, the information is sent over the Internet as manageable packets. Every packet is alloted a port number that will interface it to its endpoint.
A packet that has both a distinctive IP address and port number can be made an interpretation of from alphabetic content into electronic signs by going through the layers of the OSI model from the top application layer to the bottom physical layer. The message will then, at that point be sent over the Internet where it is gotten by the Internet service provider's (ISP) router. The router will inspect the destination address allocated to every packet and figure out where to send it.
Ultimately, the packet arrives at the customer and goes backward from the bottom physical layer of the OSI model to the top application layer. During this cycle, the routing information - the port number and IP address - is taken from the packet, consequently permitting the information to be made an interpretation of back into alphabetic content and finishing the transmission process.
Uses of the internet
As a general rule, the Internet can be utilized to convey across huge or little distances, share data from any spot on the planet and access data or answers to practically any question in minutes.
Some particular instances of how the Internet is utilized include:
Social media and content sharing
Email and different types of correspondence, like Internet Relay Chat (IRC), Internet telephony , instant messaging,video conferencing
Training and personal development through admittance to online degree programs, courses and workshops and
looking for occupations - both the employer and candidate utilize the Internet to post open positions, go after jobs and enlist people found on social networking sites like LinkedIn.
Different instances include:
- Online discussion groups and forums
- Online dating
- Online gaming
- Research
- Reading electronic newspapers and magazines
- Online shopping, or e-commerce.
Contrast between the World Wide Web and the Internet
The vital contrast between the Internet and the World Wide Web (WWW or the Web) is that the Internet is a worldwide association of networks while the Web is an assortment of data that can be gotten to utilizing the Internet. All in all, the Internet is the infrastructure and the Web is an assistance on top.
The Web is the most broadly utilized piece of the Internet. Its extraordinary component is hypertext, a technique for instant cross-referencing. In most Web sites, certain words or expressions show up in text of an unexpected shading in comparison to the rest; regularly this content is likewise underlined. At the point when a client chooses one of these words or expressions, they will be moved to the connected site or page. Buttons, pictures, or portions of pictures are likewise utilized as hyperlinks.
The Web gives admittance to billions of pages of data. Web browsing is done through a Web browser, the most mainstream of which are Google Chrome, Firefox and Internet Explorer. The presence of a specific Web site may fluctuate somewhat relying upon the browser utilized. Later or more refreshed forms of a specific browser can deliver more perplexing animation, virtual reality, sound and music files.
Security and the Internet
A lot of data, both public and private, are gathered across the Internet, freeing clients up to the danger of data breaches and other security threats. Hackers and crackers can break into networks and systems and take data, for example, login data or bank and credit card account records. A few steps that can be taken to ensure online privacy include:
- Introducing antivirus and antimalware
- Making difficult, varied passwords that are difficult to figure.
- Utilizing a virtual private network (VPN) or, at any rate, a private browsing mode, for example, Google Chrome's Incognito window.
- Just utilizing HTTPS
- Making all social media accounts private..
- Deactivating autofill.
- Turning off the device's GPS
- Updating cookies so an alert is sent anytime a cookie is installed
- Logging out of accounts rather than simply shutting the tab or window.
- Utilizing alert with spam emails and never opening or downloading content from obscure sources.
- Utilizing caution while getting to public Wi-Fi or hotspots.
Furthermore, there is a component of the Internet called the dark web. The dark web is covered up and difficult to reach through standard browsers. All things considered, it utilizes the Tor and I2P browsers which permit clients to remain altogether unidentified. While this obscurity can be an incredible method to ensure an online client's security and free discourse or for the government to keep classified data covered up, the dark web additionally establishes a climate that works with cybercrime, the transfer of unlawful merchandise and terrorism.
Social effect of the Internet
The social effect of the Internet can be viewed as both positive and negative. On one side, individuals contend that the Internet has expanded the danger of disengagement, distance and withdrawal from society, highlighting expansions in an emotional reaction called FOMO, or the fear of missing out. On the opposite side, individuals accept the Internet to have had the contrary impact on society, contending that the Internet increments community commitment, amiability and the power of connections.
Regardless of whether the effects are fortunate or unfortunate, the Internet has changed the manner in which society associates and interfaces. One illustration of progress is the expanded spotlight on self-improvement and a decrease in a community that is controlled by work, family and space. Individuals are currently building social connections dependent on singular interests, ventures and qualities. Communities are being framed by similar people not only offline and face to face, however through the Internet and the large number of online conditions which it makes and offers. Social networking sites - like Facebook and LinkedIn - have become the favoured stages for both businesses and people hoping to play out a wide range of undertakings and speak with others.
Advantages of the Internet
Advantages of the Internet include:
- Admittance to perpetual data, information and schooling.
- An expanded capacity to impart, associate and offer.
- The capacity to work from home, team up and access a worldwide workforce.
- The opportunity to sell and bring in cash as a business or person.
- Admittance to a limitless stockpile of entertainment sources, like films, music, recordings and games.
- The capacity to enhance the effect of a message, permitting charities and different associations to contact a more extensive crowd and increment the aggregate sum of donations.
- Admittance to the internet of things (IoT), which permits home appliances and gadgets to interface and be controlled from a PC or cell phone.
- The capacity to save information and effectively share records with cloud
- The capacity to screen and control individual accounts in a flash, for example, bank accounts or credit card bills.
History of the Internet
The ARPANet, the antecedent of the Internet, was first sent in 1969. In 1983, the ARPANet progressed into utilizing the TCP/IP open networking protocol suite and in 1985, the National Science Foundation Network (NSFN) planned the network to interface college computer science divisions around the country.
Interchanges over the Internet significantly worked on in 1989 when the hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) was made, enabling diverse PC stages to associate with a similar Internet sites. In 1993, the Mosaic Web browser was made.
The Internet has proceeded to develop and advance over the course of the long stretches of its reality. IPv6, for instance, was intended to expect colossal future extension in the quantity of accessible IP addresses. In a connected turn of events, the IoT is the blossoming climate wherein practically any element or article can be given with a unique identifier (UID) and the capacity to move information automatically over the Internet.